Mental Health Stats: Shocking Trends & What You Need to Know
Feeling overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information surrounding mental health statistics? You're not alone. It can be difficult to make sense of the numbers and understand what they truly mean. This article aims to provide a clear and comprehensive overview of the key mental health data, trends, and insights you need to know.
Understanding Mental Health Prevalence
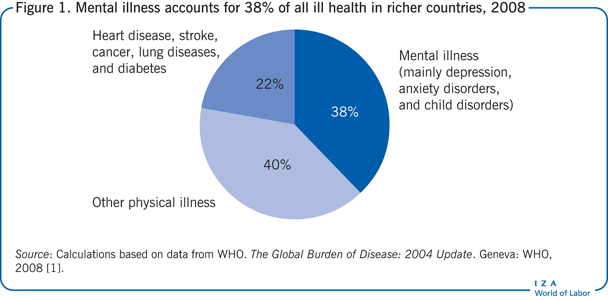
Understanding the mental health prevalence is crucial for resource allocation, policy development, and public health initiatives. Mental illness statistics paint a picture of the scope of the problem, helping us understand how many people are affected by various conditions and how this varies across different populations.
Mental health prevalence varies significantly based on age, gender, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and geographic location. For example, young adults often experience higher rates of anxiety and depression compared to older adults. Similarly, individuals from marginalized communities may face additional stressors that contribute to mental health challenges.
Factors Influencing Prevalence Rates
Several factors contribute to the varying rates of mental health prevalence. These include:
- Socioeconomic factors: Poverty, unemployment, and lack of access to resources can significantly impact mental well-being.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to trauma, violence, and discrimination can increase the risk of developing mental health conditions.
- Genetic factors: A family history of mental illness can increase an individual's susceptibility.
It's important to consider these factors when interpreting mental illness statistics and developing targeted interventions.
The Impact of COVID-19 on Mental Health
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on mental health prevalence globally. Lockdowns, social isolation, economic uncertainty, and fear of infection have contributed to increased rates of anxiety, depression, and substance use. Statistics show a significant rise in mental health issues, especially among young people and frontline workers.
Mental Health Demographics: Who is Affected?
Mental health demographics provide a deeper understanding of which populations are most vulnerable to mental illness. Analyzing these demographics helps identify disparities in access to care and tailor interventions to meet the specific needs of different groups.
Understanding mental health demographics is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. For instance, knowing that certain racial or ethnic groups face higher rates of specific mental illnesses allows for culturally sensitive interventions and outreach programs.
According to a 2023 study, LGBTQ+ individuals report significantly higher rates of mental health conditions compared to their heterosexual and cisgender counterparts. This highlights the need for targeted support and resources for this community.
| Demographic Group | Prevalence of Mental Illness (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Young Adults (18-25) | 25-30% |
| Adults (26-49) | 20-25% |
| Adults (50+) | 15-20% |
| LGBTQ+ Individuals | 35-45% |
Exploring Mental Health Trends
Examining mental health trends over time reveals important insights into the evolving landscape of mental illness. Tracking these trends allows us to identify emerging challenges, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and anticipate future needs.
One significant mental health trend is the increasing awareness and acceptance of mental illness. More people are willing to talk about their struggles and seek help, reducing the stigma associated with mental health conditions. However, despite this progress, significant barriers to care still exist.
The Role of Technology in Mental Health
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in addressing mental health needs. Teletherapy, mental health apps, and online support groups are making mental healthcare more accessible and convenient. However, it's important to ensure that these technologies are evidence-based and address privacy concerns.
Rising Rates of Anxiety and Depression
Statistics show a concerning trend of rising rates of anxiety and depression, particularly among young people. Factors contributing to this trend include increased stress, social media pressures, and economic uncertainty. Early intervention and prevention efforts are crucial to address this growing problem.
Analyzing Mental Health Impact
The mental health impact extends far beyond individual suffering. Mental illness can affect relationships, academic performance, work productivity, and overall quality of life. Understanding the broader impact of mental health conditions is essential for advocating for increased resources and support.
The economic burden of mental illness is substantial, including costs associated with treatment, lost productivity, and disability. Investing in mental healthcare and prevention programs can lead to significant cost savings in the long run.
"Mental health is not merely the absence of mental illness. It is an integral part of our overall health and well-being." - World Health Organization
Mental health impact also includes the social stigma associated with mental illness. Stigma can prevent people from seeking help and can lead to discrimination and social isolation. Efforts to reduce stigma are essential for creating a more supportive and inclusive society.
Mental Health Treatment Statistics and Access to Care
Mental health treatment statistics reveal important information about the availability, utilization, and effectiveness of mental healthcare services. Analyzing these statistics helps identify gaps in care and inform strategies to improve access and quality of treatment.
A significant challenge in mental healthcare is the limited access to services, particularly in rural and underserved communities. Many individuals face barriers such as cost, lack of insurance, transportation difficulties, and cultural stigma.
| Metric | Value (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Percentage of adults with mental illness who receive treatment | 40-50% |
| Percentage of youth with mental illness who receive treatment | 20-30% |
Increasing access to evidence-based treatments, such as therapy and medication, is crucial for improving outcomes for individuals with mental illness. Early intervention is also essential, as it can prevent mental health conditions from becoming more severe and debilitating.
Global Mental Health Statistics
Global mental health statistics highlight the worldwide burden of mental illness. Mental health conditions are a leading cause of disability globally, affecting millions of people of all ages and backgrounds. Understanding the global picture is essential for international collaboration and resource allocation.
Mental health challenges are particularly acute in low- and middle-income countries, where resources are often limited and access to care is scarce. Addressing the global mental health crisis requires a coordinated effort from governments, organizations, and individuals.
Cultural factors also play a significant role in global mental health statistics. Beliefs and attitudes about mental illness vary widely across different cultures, influencing help-seeking behaviors and treatment outcomes.
Identifying Mental Health Risk Factors
Understanding mental health risk factors allows for proactive identification of individuals at higher risk and the implementation of preventive measures. These factors can range from genetic predispositions to environmental influences.
Common Risk Factors
Here are some common mental health risk factors to be aware of:
- Family history of mental illness
- Traumatic experiences
- Chronic medical conditions
- Substance abuse
- Social isolation
FAQ
Here are some frequently asked questions about mental health statistics:
- Where can I find reliable mental health data? You can find reliable data from organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO), the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- How is mental health prevalence measured? Mental health prevalence is typically measured through surveys, clinical interviews, and administrative data from healthcare systems.
- What are the limitations of mental health statistics? Mental health statistics can be limited by factors such as stigma, underreporting, and variations in diagnostic criteria across different settings.
Understanding mental health statistics is crucial for promoting mental well-being and improving access to care. By staying informed and advocating for change, we can create a more supportive and equitable society for individuals with mental health conditions. Do you have any questions or personal experiences related to mental health that you'd like to share? Please leave a comment below; your voice matters!